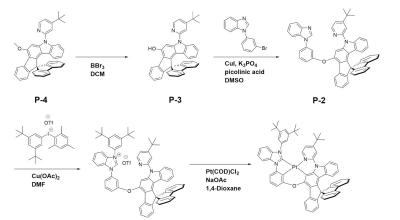
BNTPA molecule shows promise for long-lasting high-efficiency deep red MR-TADF emitters
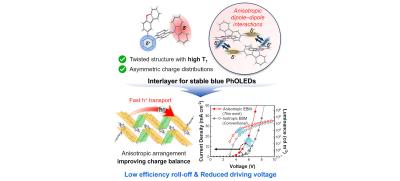
Researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC and the Beijing Information Science and Technology University (BISTU), have developed a new strategy for the design of deep red MR-TADF OLED emitters, that offers high efficiency, good color emission and long lifetimes.
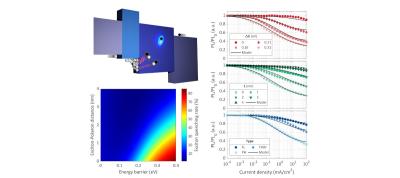
The researchers report they have developed a new deep red (0.657,0343 CIE) OLED emitter material that achieves high efficiency, over 43% EQE, which they say is the most efficient MR-TADF red emitter.