Japan Display (JDI) is a small/medium display maker, formed in September 2011 by the merger of Sony's, Toshiba's and Hitachi's display businesses and funded by Japan's government fund Innovation Network Corporation (INCJ), which holds 70% of the shares.
JDI considers OLEDs to be the core technology of the next generation small size and medium size displays, and in 2017 the company announced that it is going to perform a "last-chance" restructuring to focus on OLEDs as there is "no future for the smartphone panel business without OLED". The company however didn't achieve mass production of displays beyond small wearable AMOLEDs (which it supplies to Apple).
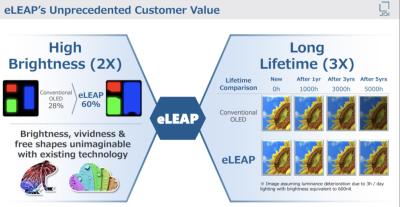
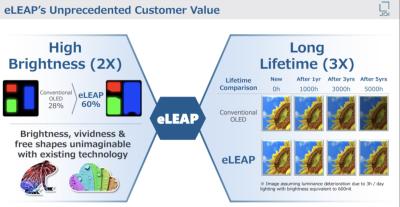
In 2022, JDI announced a new OLED deposition process which they refer to as eLEAP, that the company says is a breakthrough OLED production process. The company seems now focused on commercializing this technology, and in 2024 it announced it started to produce laptop eLEAP AMOLED displays in its 6-Gen line in Mobara.
In August 2014 JDI, together with Sony, Panasonic and INCJ, launched JOLED to develop and produce printed OLED panels. In December 2016 JDI raised $635 million from INCJ to increase its stake at JOLED, and in 2020 the company raised $935 million from Ichigo. In October 2019 Japan Display announced it has started to produce OLED displays - likely indeed this is low volume production for Apple's wearables. In 2023 JOLED filed for bankruptcy, and JDI took over all of its assets.
3-7-1 Nishi-shinbashi
Minato-ku
Tokyo
105-0003
Japan
Japan Display announced a strategic investment in OELDWorks, to jointly build an advanced OLED production line in the US
Japan Display (JDI) made an interesting announcement today, saying that it has made a strategic investment in OLEDWorks, and now owns 6.69% of the company. The two companies are also planning to build an advanced OLED production line in the US, targeting high-performance displays for the defense, automotive and medical industries.
JDI did not disclose much else, beyond saying that in addition to the manufacturing hub, it will alsop build an advanced display R&D center in the US, together with OLEDWorks. JDI does seem to emphasize OLEDWorks' multi-stack architecture, which maybe means that this technology will be used in the upcoming production line.
Japan Display, Innolux and CarUX to bring eLEAP automotive displays to market
Japan Display announced a new strategic partnership with Taiwan-based Innolux and CarUX (Innolux's automotive display company) to bring eLEAP OLED displays to the automotive market.
The three companies did not disclose a lot of details, but it seems as in this partnership JDI will produce the eLEAP OLED displays while CarUX will market and sell these displays to its automotive customers. The first display that JDI will produce will be a 32" 1,000 nits 6460x880 (205 PPI) AMOLED display on an HMO (high-mobility oxide) backplane.
Applied Materials launches a maskless OLED production technology, to support 8-Gen high efficiency OLED deposition and encapsulation
Applied Materials announced a technology, branded as MAX OLED that enables OLED display production on large glass substrates, aiming to provide a cost-effective solution to produce TV and TV displays. Applied developed and patented a new OLED pixel architecture and a "dramatically different manufacturing approach" that the company says enables brighter, clearer, more energy-efficient and longer-lasting.
Applied's new MAX OLED systems can scale from 6-Gen substrates to 8-Gen substrates, supporting the new wave of IT OLED production lines. Applied says that its new solution has strong customer interest - and already achieved repeat orders from several leading display makers (see below). Specifically, Applied announced that it will supply an R&D system to Samsung Display that will test the new production technology for its AMOLED and QD-OLED production technologies.
Japan Display has not yet signed an agreement to build its 8.7-Gen eLEAP production line in Wuhu
In 2022, Japan Display (JDI) announced that it has developed a "historic breakthrough in display technology" - a new OLED deposition process which they refer to as eLEAP, that is said to be cost effective and can be used to create freeform OLEDs that are brighter, more efficient, and longer lasting compared to OLEDs produced using mask evaporation (FMM).
JDI is building a small-scale 6-Gen eLEAP production line in Mobara, Japan, with plans to begin production before the end of 2024. The company is also planning to establish a 8.7-Gen eLEAP fab in Wuhu, Anhui Province, China, and in April 2024 it said it hopes to sign the agreement with Wuhu's Economic and Technical Development Zone (WEDZ) by October 2024. Now JDI has made a rather confusing announcement, saying that while it decided not to extend its current MOU with the WEDZ.
Apple looks to adopt a TFT AMOLED for its future entry-level MR headset
There's an interesting report in Korea that claims that Apple is developing an entry-level MR headset, and is looking to adopt TFT based AMOLED displays, as opposed to the currently-used OLED microdisplays. It is reported that both JDI and Samsung are in talks with Apple, and have been requested to develop lower-cost TFT AMOLEDs with a pixel density of 1,500 PPI (down from 3,400 PPI high-end Sony microdisplays used in the Vision Pro).
It is understood that JDI has already developed the technology and produced 1,500 PPI samples for Apple. Interestingly it is reported that the JDI displays uses Sony's technology, although it is not stated which technology exactly. Samsung meanwhile is also developing 1,500 PPI AMOLEDs at its A2 fab. Apple's target is to release the headset at around 2026-2027 and by then it is likely that more OLED producers (such as LG Display) will develop similar displays.
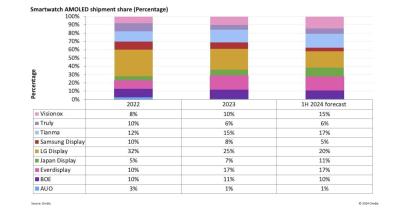
Omdia: adoption of OLEDs in smartwatch applications grows to 37% of the market
Omdia says that it expects the global smartwatch display market to reach 359 million units in 2024 (up from 259 million units in 2022). OLEDs hold a 37% market share (132 million units).
Omdia says that the leading smartwatch OLED producers, in the first half of 2024, are LG Display (Apple's main supplier), Everdisplay and Tianma - which together hold a 53% market share. China-based wearable OLED production accounts to 64% of the total market.
Japan Display to start producing eLeap laptop displays at its 6-Gen Mobara fab, ahead of schedule
In 2022, Japan Display (JDI) announced that it has developed a "historic breakthrough in display technology" - a new OLED deposition process which they refer to as eLEAP, that is said to be cost effective and can be used to create freeform OLEDs that are brighter, more efficient, and longer lasting compared to OLEDs produced using mask evaporation (FMM).
JDI is planning to establish a 8.7-Gen eLEAP fab in China, and it is also building a smaller-scale 6-Gen eLEAP production line in Mobara, Japan. The company announced that the 6-Gen Mobara fab is advancing ahead of schedule, and production of eLEAP panels will begin before the end of 2024. JDI developed 14" laptop panels that are three times brighter than other OLEDs (at 1,600 nits), and is also targeting smartwatches, smartphones and automotive displays. JDI is also looking into adopting a tandem structure, to increase brightness even further to 3,000 nits.
Japan Display again delays its plans to build a 8.7-Gen eLEAP AMOLED line in China
In 2022, Japan Display (JDI) announced that it has developed a "historic breakthrough in display technology" - a new OLED deposition process which they refer to as eLEAP, that is said to be cost effective and can be used to create freeform OLEDs that are brighter, more efficient, and longer lasting compared to OLEDs produced using mask evaporation (FMM).
Japan Display announced an agreement with China-based LCD maker HKC Corp to mass produce panels by 2025 in China, based on JDI's technology, but the plan was later cancelled, and JDI said it will establish its own factory in China. This project saw delays and was scaled-down in December 2023, and yesterday JDI announces that it again delays the project - now hoping to sign the agreement with the Wuhu Economic and Technological Development Zone by October 2024.
Japan Display delays and scales back its plan to mass produce eLEAP AMOLED displays in China
In 2022, Japan Display (JDI) announced that it has developed a "historic breakthrough in display technology" - a new OLED deposition process which they refer to as eLEAP, that is said to be cost effective and can be used to create freeform OLEDs that are brighter, more efficient, and longer lasting compared to OLEDs produced using mask evaporation (FMM).
Japan Display announced an agreement with China-based LCD maker HKC Corp to mass produce panels by 2025 in China, based on JDI's technology, but the plan was later cancelled, and JDI said it will establish its own factory in China. The company was negotiating with the Wuhu Economic and Technological Development Zone (in Anhui Province), aiming to establish two eLEAP AMOLED production lines by 2025. JDI hoped to sign the formal agreement before the end of 2023.
JDI now announced that it is scaling back its plans. Originally JDI aimed to establish two production lines: one 6-Gen (with a capacity of 10,000 monthly substrates) and one 8.7-Gen (30,000 monthly substrates). Now JDI decided to reduce its plans, to a single 8.7-Gen fab. In addition, it estimates it will sign the final contract in March 2024. The 8.7-Gen line will start mass production in December 2026.
Japan Display progresses with its plans to produce eLEAP AMOLEDs in China, also looking into production in India
In 2022, Japan Display (JDI) announced that it has developed a "historic breakthrough in display technology" - a new OLED deposition process which they refer to as eLEAP, that is said to be cost effective and can be used to create freeform OLEDs that are brighter, more efficient, and longer lasting compared to OLEDs produced using mask evaporation (FMM).
Japan Display announced an agreement with China-based LCD maker HKC Corp to mass produce panels by 2025 in China, based on JDI's technology, but the plan was later cancelled, and JDI said it will establish its own factory in China. The company now says that it is progressing with its negotiations with the Wuhu Economic and Technological Development Zone (in Anhui Province), and the hope is to reach a final agreement will be reached by the end of the year. Interestingly, JDI also says that it is considering building an eLEAP AMOLED fab in India, but we do not have more details.
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page