Deuterium's Impact on OLED Displays
This is a sponsored post by Clearsynth
In the ever-evolving field of display technology, OLED displays have emerged as a prominent player due to their ability to deliver stunning visuals, energy efficiency, and flexibility.
One key component that has contributed to the success of OLED displays is deuterium, a stable isotope of hydrogen. Deuterium's impact on OLED displays can be seen in its potential to magnify these devices' overall performance and lifespan.
- Deuterium (2H, D): Discovered in 1931 by H. Urey, who won the Nobel Prize in 1934 and named it Deuterium.
- Stable, nonradioactive isotope of hydrogen with one proton and one neutron in its nucleus
- Natural abundance of 0.015% of hydrogen atoms on Earth
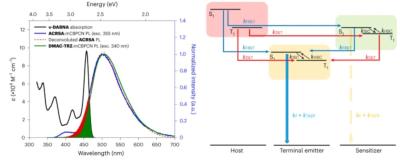
Deuterium, a heavier isotope than hydrogen, offers several advantages in OLED displays. First and foremost, deuterium is known to increase the brightness and efficiency of OLED displays. TV Panel manufacturers use OLED materials to generate the 3 primary colours (red, green, blue) in full-colour display. They had a challenge of large electronic power consumption for blue OLED relative to green and red OLEDs. This has been successfully overcome by deuterated blue OLED emitters which provide higher stability and prolonged lifetime, resulting in greater brightness and efficiency.