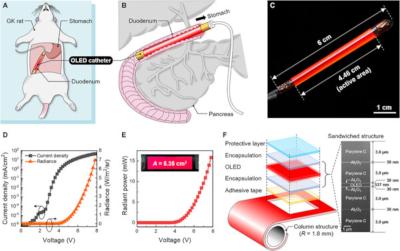
Researchers develop a blue fluorescent OLED device with ultra-low turn-on voltage
Researchers from the Tokyo Institute of Technology, Osaka University, University of Toyama and Shizuoka University have developed a fluorescent blue (462 nm) OLED device that features an ulta-low turn-on voltage of 1.47 V (at 100 nits). The researchers say this is very low, as similar commercial blue devices typically need around 4 V.
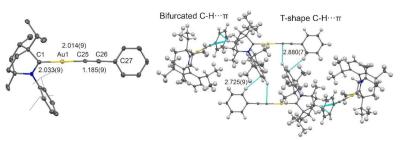
To achieve that low turn-on voltage, the researchers built a new device, as they realize that the choice of materials significantly influences the device's turn-on voltage. The device itself is an upconversion OLED.