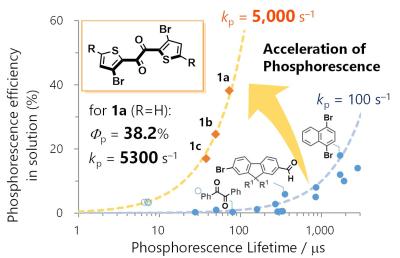
Researchers from Osaka University have found that thienyl diketone, a new organic molecule, shows high-efficiency phosphorescence, and one that is more than ten times faster than traditional organic phosphorescence materials. Such a material could hold promise for highly-efficient phosphorescence emission without the use of heavy metals.
The researchers explain that phosphorescence occurs when a molecule transitions from a high-energy state to a low-energy state, and it often competes with non-radiative processes (i.e. heat generation instead of light). This competition with the non-radiative process leads to slow phosphorescence and lower efficiency. This is solved by adding heavy metal into the emitter - but this new breakthrough achieves fast emission without the heavy metal.
This is an exciting discovery, but there's much research ahead to explore the potential and learn of the applicability of the new material in real applications.